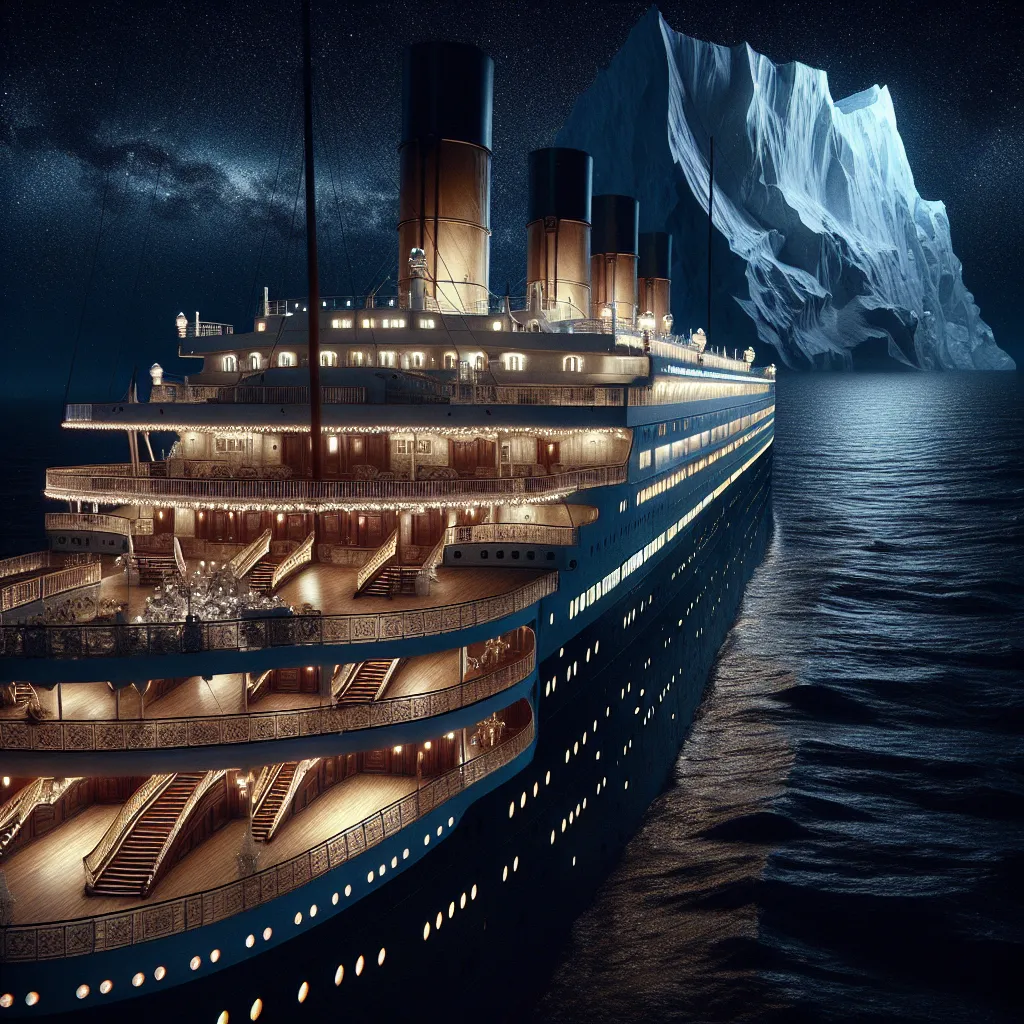
The news of the Titanic disaster broke on April 16, 1912, just a day after the tragedy. Devastated families of the victims were eager for answers. How could the “unsinkable” Titanic meet such a fate? Designed to be both the most luxurious and safest ship of its time, the Titanic was supposed to stay afloat even if hit by another vessel. Yet, it sank within two hours of striking an iceberg.
Two weeks later, a public inquiry was launched to determine if the disaster could have been prevented and to identify who might be responsible for the loss of 1,523 lives. Bruce Ismay, the chairman of White Star, the company that owned the Titanic, was one of the key witnesses. Along with him, other vital testimonies came from Harold Bride, the wireless operator, and Charles Lightoller, the most senior surviving officer, as most of the crew had perished.
During the inquiry, it was revealed that Ismay had held a meeting with chief designer Alexander Carlisle two years before the Titanic’s launch. This meeting led to significant design decisions, including reducing the height of the watertight compartments and installing a grand staircase instead. Despite warnings, only 16 lifeboats were installed, though the original recommendation was 48.
Meanwhile, 2,000 miles away, a glacier in West Greenland released an iceberg, one of 40,000 born each year in the region. This iceberg, destined for the North Atlantic shipping lanes, began a journey that would eventually intersect with the Titanic’s ill-fated voyage. The iceberg moved north before starting its journey southward.
As work progressed on the Titanic, the shipbuilders faced a mix of tradition and innovation. The steel hull was held together by iron rivets in its curved sections due to the limitations of the available machinery. This practice, widespread at the time, went unquestioned until nearly a century later. An expedition in 1996 found that using iron rivets made the ship more vulnerable, which contributed to its sinking.
Upon completion, the Titanic was hailed as a marvel, but hidden flaws in its construction and a rapidly approaching iceberg spelled disaster. By the summer of 1911, the 18-month-old iceberg had started moving towards the Atlantic, while work on the Titanic continued in anticipation of its maiden voyage.
The Titanic was captained by Edward John Smith, a highly respected and experienced commander. It was to be his final voyage before retirement. Initially scheduled to set sail in March, the journey was postponed to mid-April due to unforeseen delays, inadvertently placing it in peak iceberg season.
By mid-April 1912, the iceberg, despite massive odds, had traveled close to Newfoundland’s east coast. Still weighing over half a million tons, it continued its southward drift. The collision that sunk the Titanic was not just a result of the ship’s design flaws but also a culmination of unfortunate timing and overlooked dangers in the shipping lanes.